What Are Bad SEO Practices?
Bad SEO practices are those that violate search engine guidelines or negatively affect the user experience. These practices undermine the primary goal of search engines and AI tools: to help users find helpful, relevant, and trustworthy information.
Some bad SEO practices are unintentional, often stemming from outdated tactics—like keyword stuffing. Although frequent keyword repetition once helped sites appear higher in Google, it reduces readability and can lower visibility.
Here’s an example of keyword stuffing:

Plus, repeatedly using the same query can prevent you from gaining visibility in AI platforms like ChatGPT. Those tools use a query fan-out process that considers the multitude of ways people speak about a given topic when seeking relevant sources.
Other bad SEO practices are intentional and manipulative, such as using private blog networks (PBNs), cloaking, or buying spammy backlinks. These methods may deliver short-term results but typically result in penalties from search engines.
Consequences of Bad SEO
Here’s what can happen if you fall into adverse SEO habits:
- Drop in visibility: Search engines and AI search tools aim to show high-quality, user-focused content. If your site relies on outdated or manipulative SEO tactics, you’re unlikely to show prominently.
- Less traffic: When you aren’t as visible in search results and AI tools, you’ll inevitably get less traffic to your site. And that also means fewer potential customers or clients.
- Damage to your brand’s reputation: Low-quality or deceptive content doesn’t just impact SEO—it can also harm your credibility. Users notice when a website feels spammy, unreliable, or frustrating to use.
- Google penalties: Engaging in deceptive tactics can trigger manual penalties from Google. Recovering from these penalties is challenging and time-consuming.
- Competitors gain advantage: If your site loses visibility, your competitors can quickly capitalize on it
8 Bad SEO Practices (with Examples)
We surveyed 58 SEOs and content marketers on LinkedIn about the most harmful SEO practices. Below are the results, ordered from most to least problematic.
| Bad SEO Practice | % Saying It’s Most Problematic |
| Creating unhelpful content that lacks expertise | 29.3% |
| Over-optimizing for search | 24.1% |
| Using private blog networks | 12.1% |
| Delivering a poor user experience | 15.5% |
| Manipulating search engines with cloaking | 6.9% |
| Publishing generic, AI-generated content | 6.9% |
| Having duplicate content | 3.4% |
| Relying on reputation abuse | 1.7% |
1. Creating Unhelpful Content That Lacks Expertise
Content that doesn’t provide real value or expertise often struggles to rank highly in search engines. And it’s less likely to show in AI search as well.
From our survey, 29.3% of the respondents identified this as the most problematic bad SEO practice.
Google prioritizes content that’s helpful, trustworthy, and authored by experts. That also matters for AI systems when you consider they often use Google results.
So, if you’re writing about fitness tips and simply rehash information from existing articles (like “do cardio” and “lift weights”) without offering unique insights, search engines, AI tools, and users will likely see your page as low-value.
What to Do Instead
- Write from experience: Share what you’ve personally done, tested, or learned. If you don’t have direct experience, interview subject matter experts and include their insights to provide depth. For example, if you're writing about growing an email list, talk about tactics you've actually used. Like how publishing a research report helped you grow to a certain number of subscribers.
- Use original data: Run surveys, analyze your own performance metrics, or pull insights from internal reports. Even small data points can make your content stand out. For example, a financial advisor writing about investment strategies could include survey data from clients on risk preferences and asset choices.
- Find a unique angle: Look for what’s missing from competing content, then fill that gap with your own perspective or helpful additions. For example, instead of a generic “How to Use ChatGPT” guide, focus on specific use cases across relevant industries.
Further reading: Quality Content: What It Is + 10 Actionable Tips for Success
2. Over-Optimizing for Search
When content is written more for search engines and AI systems than people, it often performs poorly by all measures. And 24.1% of our survey participants flagged over-optimization as a significant concern.
Over-optimization occurs when content is so focused on showing up in search that it becomes unnatural for readers. This can happen through excessive keyword use, awkward anchor text, or unhelpful and repeated internal links.
Over-optimized content often comes off as clunky, robotic, or spammy. It disrupts the reading flow, hurts user experience, and may even trigger Google penalties.
What to Do Instead
- Write for humans first: Focus on delivering real value to readers—not just optimizing your content. For example, a marketing agency could publish a guide on how to build a content strategy with clear and actionable steps, real examples, and natural use of target keywords/prompts.
- Link to relevant pages when valuable: Only use internal links when they’re relevant and genuinely help the reader explore related topics or take action. For example, a skincare blog post on how to treat dry skin could link to its moisturizer guide within a section on hydration.
3. Using Private Blog Networks
A private blog network (PBN) is a network of websites built to link to your site to improve its search performance.

SEOs build PBNs by either setting up new sites or purchasing high-authority domains. These sites then link to your site to increase its authority.
Though PBNs can sometimes improve performance, using them is high risk.
If Google catches you trying to manipulate performance in this way, your site could be penalized or even removed from search results. Of our survey participants, 12.1% highlighted this tactic as problematic.
Edward White, Founding Growth Lead at Brightwave, faced this issue firsthand in a previous role when his team decided to test out a third-party SEO service:
“Within weeks, I noticed a suspiciously fast spike in referring domains. A deeper audit revealed the sites were part of a disguised PBN. We cut ties immediately and submitted a disavow file. Fortunately, the domains hadn’t yet been indexed, so we avoided penalties.
As a result, Edward and his team rethought how to evaluate link sources and made sure to vet every backlink strategy.
“We also prioritized digital PR over synthetic backlinking. After the change, our organic traffic grew steadily with lower volatility.”
What to Do Instead
Focus on building authority in a legitimate and sustainable way:
- Create link-worthy content: Publish unique and valuable resources that others want to reference. For example, a cybersecurity company could release a research report on phishing attacks across Europe that tech blogs and news outlets want to link to because it offers insights not found elsewhere.
- Contribute guest posts to reputable sites: Submit high-quality posts to high-authority publications in your niche. For example, if you’re in ecommerce, you could submit a guest post to Triple Whale.
- Run targeted link-building campaigns: Reach out to sites linking to similar competitor content and pitch yours as a better alternative. For example, you could find articles linking to an outdated guide and propose those articles link to your updated version (with expert insights and new data) instead.
- Build real relationships in your industry: Collaborate with people in your niche in ways that naturally lead to backlinks. For example, if you position yourself as a thought leader in the marketing space, you could get invited to a respected podcast. This can lead to brand mentions and links to your site.
Use Semrush’s Link Building Tool to build high-quality backlinks at scale. It helps you manage the entire process all in one place.
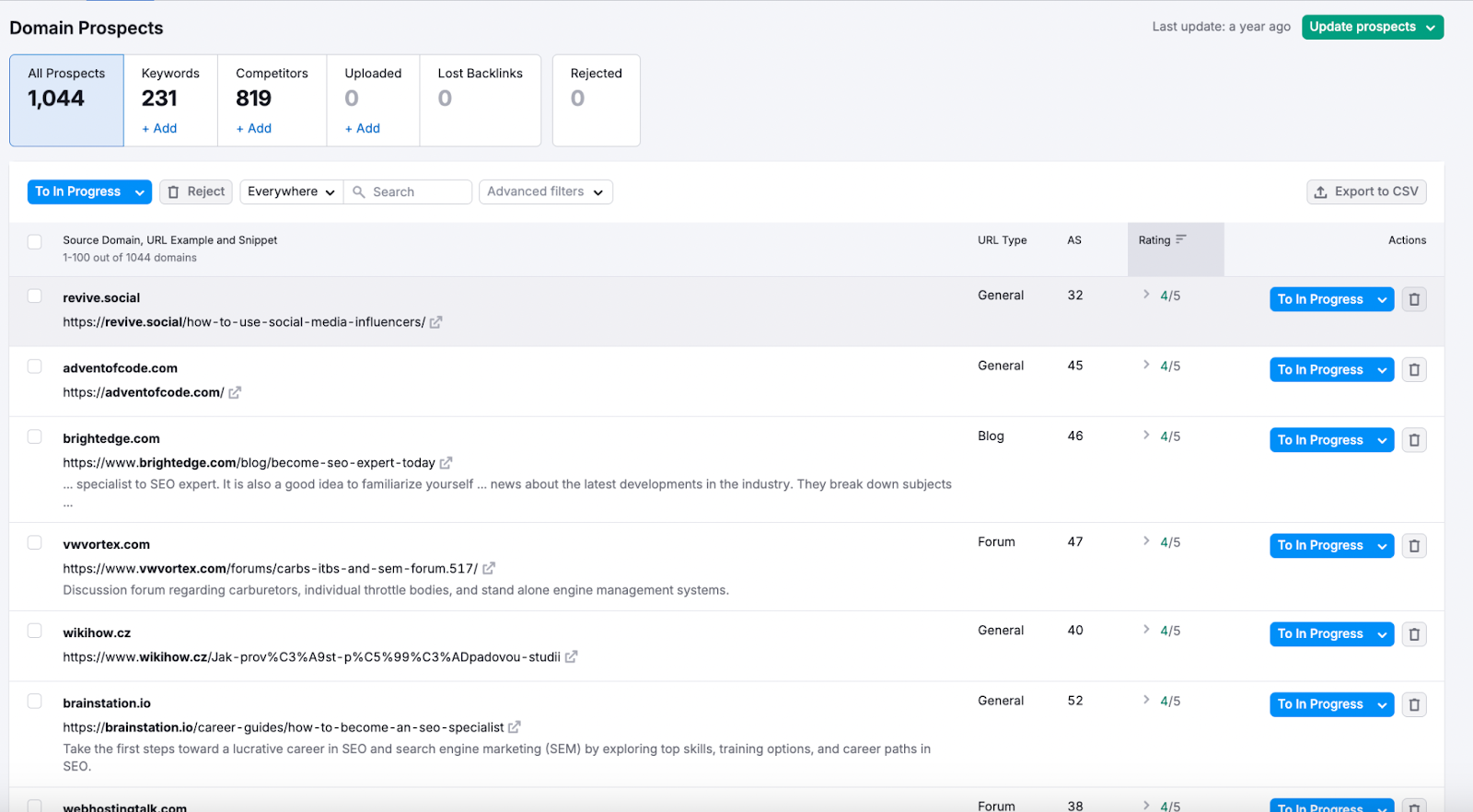
4. Delivering a Poor User Experience
Providing a poor user experience (UX) can mean long load times, mobile issues, autoplay videos, intrusive pop-ups, aggressive CTAs, sticky widgets, and more.
For instance, say a user wants to read your blog post but is confronted by a full-screen pop-up, an autoplay video, and a “tap to reveal” block. Frustrated, they click out of the page.
Almost 16% of our survey respondents identified poor UX as a major issue.
Survey respondent Becky Cockcroft, a Freelance SEO Manager, offers a useful approach for knowing whether you’re providing good UX:
"Imagine if you were the user. The real goal is to create a seamless and enjoyable experience for them—because that’s what truly drives engagement and satisfaction."
Google considers user engagement signals when determining where pages should show in results, which means those signals can also impact AI visibility. If users struggle to navigate your site or get bombarded with distractions, it’s likely to negatively impact your performance.
What to Do Instead
Make your content easy to read and navigate by:
- Prioritizing speed and mobile usability: Sites that load quickly and work well on mobile deliver a good UX. For example, you can compress product images, use lazy loading, and adopt a mobile-first layout.
- Limiting distractions: Use pop-ups, autoplay videos, and sticky elements with caution—they can frustrate users and increase bounce rates. Consider non-intrustive options like a subtle banner that appears only after a user scrolls to a certain point.
- Guiding the reader: Structure your content with logic and flow. Use visuals and clear layout choices to help users stay engaged. For example, a B2B blog can break long posts into digestible sections with descriptive headings, icon-based summaries, and inline visuals.
Use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to spot UX issues you can address to maintain your search visibility.
To start, launch the Site Audit tool and enter your domain. Click “Start Audit.”

Follow this configuration guide to set up your project. Once the audit is complete, you’ll see issues grouped into different sections.
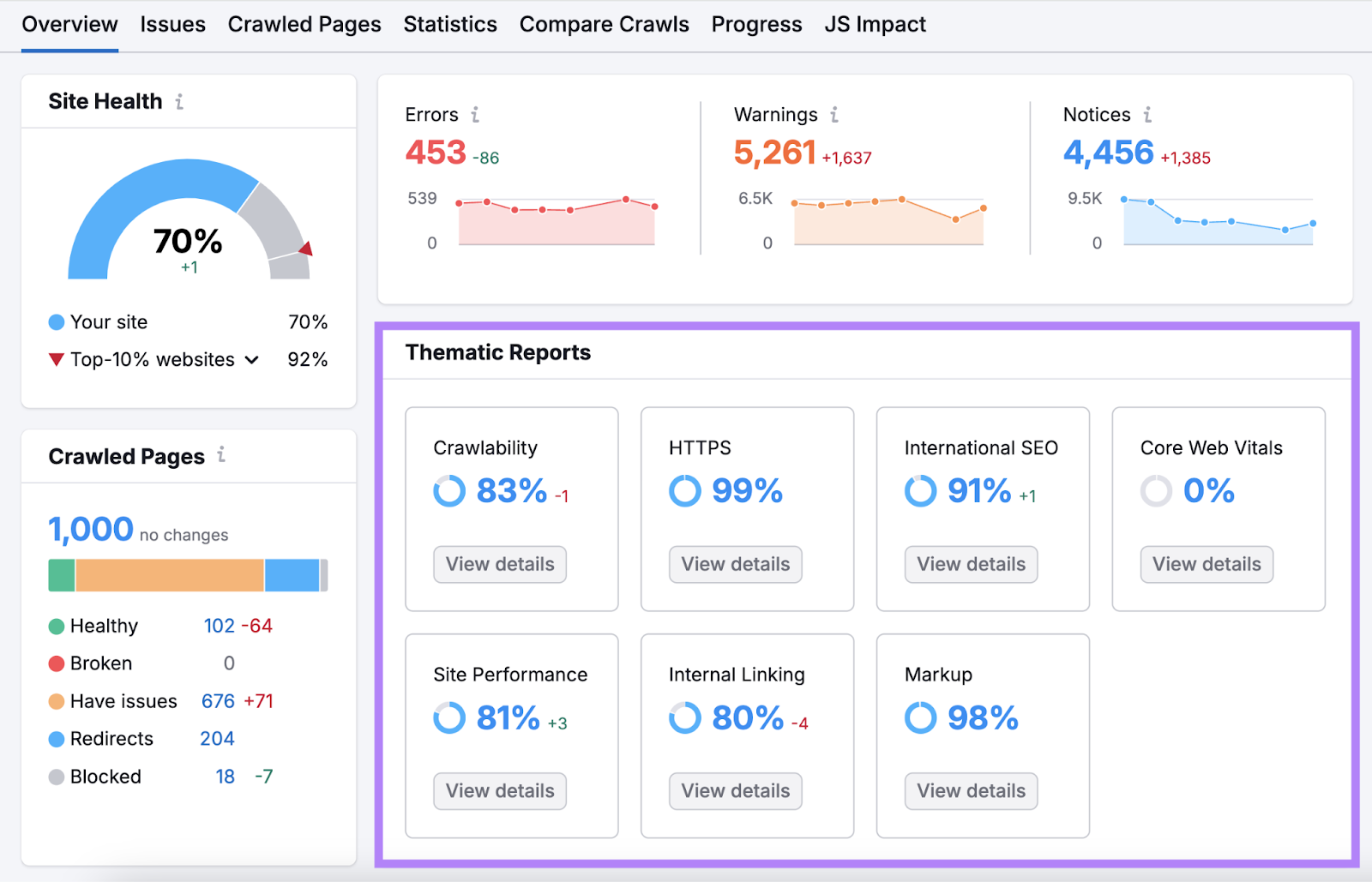
Focus on the ones that affect user experience: HTTPS, Core Web Vitals, and Site Performance.
Click “View Details” to dive deeper into each category.
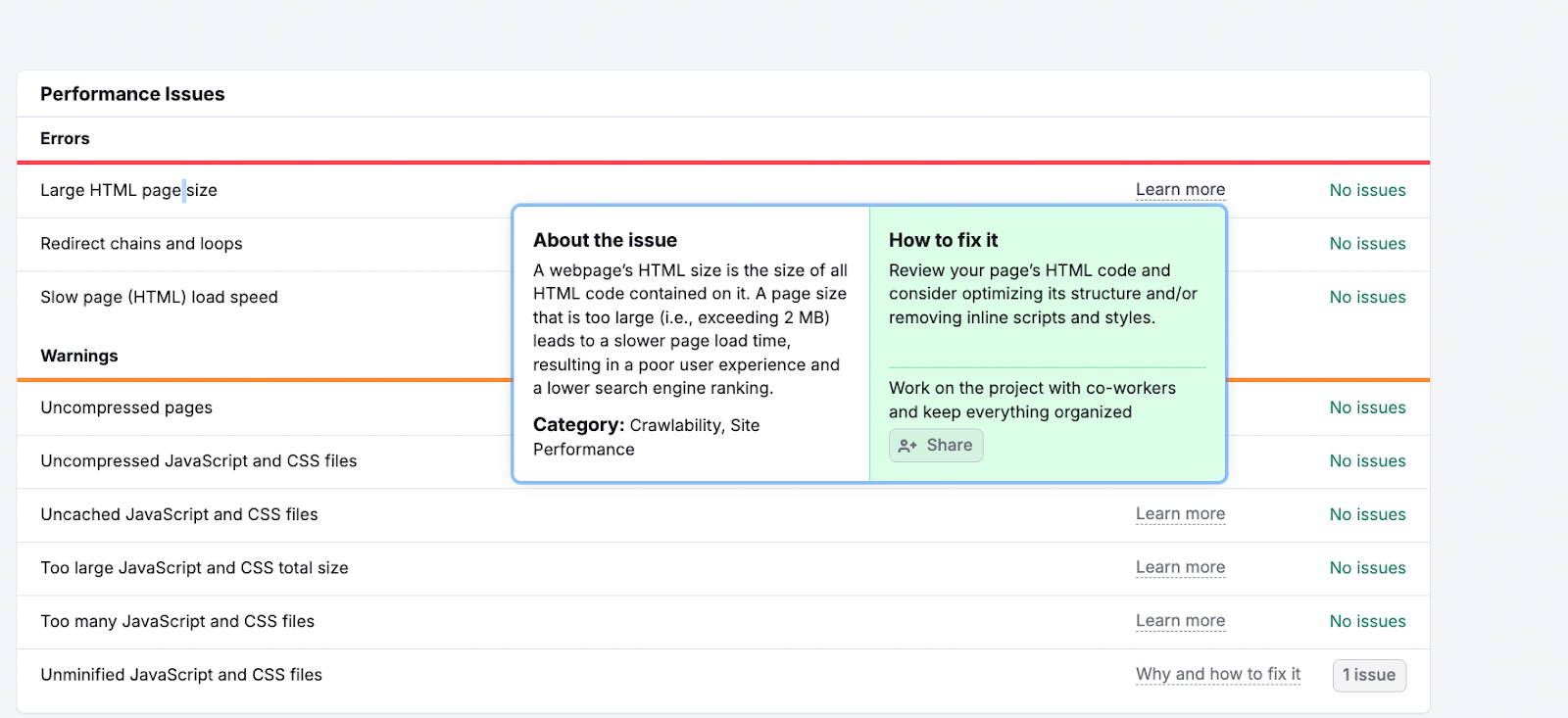
You’ll find specific issues listed along with clear, actionable steps to fix them.
5. Manipulating Search Engines with Cloaking
Cloaking is a tactic that purposely shows different content to search engines versus users. It violates Google’s guidelines and is a quick way to get penalized or even deindexed.
An example of cloaking is when a site shows Google an optimized page about training dogs. But when a user clicks the link, they’re redirected to a sales page for dog treats.
Nearly 7% of survey participants identified cloaking as a significant SEO mistake.
What to Do Instead
Avoid cloaking and instead:
- Be consistent: Show the same content to users and search engines
- Redirect responsibly: Use redirects only when necessary, and make sure they lead to relevant and expected content. For example, if you sunset a blog post on meal planning, redirect it to an updated guide on the same topic.
- Check what bots see: Use tools like Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool to confirm what pages search engines are indexing
6. Publishing Generic, AI-Generated Content
AI-generated content that lacks originality and depth can negatively affect your performance in search engines and AI tools.
Google’s helpful content update aims to prioritize high-quality, user-focused content. Low-value AI content can result in penalties and reduced visibility.
Close to 7% of our survey participants say publishing generic, AI-generated content is the most problematic bad SEO practice.
What to Do Instead
Use AI to support your content creation—not to replace it. Here’s how:
- Make meaningful edits: Go beyond surface-level tweaks. Add real examples, expert insights, and personal experience. And restructure sections, improve the logical flow, and fill in gaps AI might miss.
- Offer something original: Include unique data, original research, and expert quotes. For example, a SaaS blog can supplement an AI-generated article with stats from a recent user survey and commentary from the product team on emerging trends.
- Improve readability: Use simple language to make your content easy to follow. For example, a technical post on schema markup can be rewritten using analogies and plain English, making it easier for non-technical marketers to follow.
Use Semrush’s Content Toolkit to create high-quality content at scale. The toolkit guides you through the stages of content production, from topic ideation to publication.

When it’s done, publish or export it with just a few clicks.
7. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content pages that have identical or nearly identical content can lead to lower or even no search visibility for that content.
According to our survey, 3.4% of survey respondents identified duplicate content as a notable SEO concern.
Duplicate content can even occur without you realizing it. For instance:
- You might create a new piece of content on a topic you already have a page about
- You might publish variations of pages (such as separate U.S. and U.K. versions of a page) that are nearly identical
What To Do Instead:
There are several ways to prevent or address duplicate content:
- Set canonical tags: Use canonical URLs to tell Google which version of a page you want to appear in search results when you have similar pages. For example, an online fashion store with filtered product pages (e.g., /shoes?color=black and /shoes?size=9) can set the canonical URL to the main product page (e.g., /shoes).
- Use 301 redirects: If you have multiple pages covering the same topic, choose one primary page and redirect other variations to it. For example, a SaaS company could combine two landing pages targeting the term “CRM for small businesses” by updating one page and then redirecting the other to it.
- Specify www or non-www URLs: Clearly define whether your domain is "www" or "non-www" and be consistent
- Add hreflang tags: If your site has multiple country or language versions, use hreflang tags to clearly indicate these variations to Google to ensure the correct page appears for any given user
Easily find duplicate content on your site using Semrush’s Site Audit tool.
Once you’ve configured your project, head to the “Issues” tab and search for “duplicate content.”

Address the duplicate content by using methods like canonical tags, setting up redirects, etc.
8. Reputation Abuse
Reputation abuse involves leveraging another website’s authority to manipulate rankings.
Close to 2% of survey respondents flagged regulation abuse as the most concerning bad SEO practice.
Forbes Advisor was widely criticized for engaging in reputation abuse by capitalizing on the main domain’s authority to get high search visibility for pages covering topics outside their areas of expertise. And Forbes Advisor saw a sharp decrease in organic traffic following Google’s reputation abuse policy update at the end of 2024.

What To Do Instead:
Focus on building your own reputation. Here’s how:
- Create valuable content: Publish helpful content that clearly aligns with your expertise. For example, an HR software company could produce a guide on writing inclusive job descriptions that includes templates, research-backed tips, and DEI consultant insights.
- Be transparent: Clearly disclose any affiliate or sponsored relationships. For example, product review sites typically include a disclosure stating that the page contains affiliate links they earn a commission from.
Focus on the Latest SEO Best Practices
Ultimately, the best way to avoid bad SEO practices is to follow SEO best practices.
But mistakes still happen.
The key? Catching them in time and fixing them quickly. So your visibility and results don’t suffer.
To stop bad SEO in its tracks, regularly use the Site Audit tool.